Pressure Ulcers/Bedsores
 Pressure ulcers (PUs) acquired during hopitalization, evaluated as either Stages III or IV are considered among the eight preventable conditions identified by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). Since October of 2008, hospitals no longer receive higher Medicare payments related to the ulcer specific care of patients who acquire Stages III or IV PUs during their inpatient stay. Private insurers are also adopting these reimbursement restrictions. PUs documented in hospitalized patients are often a secondary diagnosis rather than the primary reason for hospitalization. In 2007, CMS reported 257,412 cases of secondary, Stages III or IV PUs, at a cost per case of US$43,180.
Pressure ulcers (PUs) acquired during hopitalization, evaluated as either Stages III or IV are considered among the eight preventable conditions identified by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). Since October of 2008, hospitals no longer receive higher Medicare payments related to the ulcer specific care of patients who acquire Stages III or IV PUs during their inpatient stay. Private insurers are also adopting these reimbursement restrictions. PUs documented in hospitalized patients are often a secondary diagnosis rather than the primary reason for hospitalization. In 2007, CMS reported 257,412 cases of secondary, Stages III or IV PUs, at a cost per case of US$43,180.
— Zaratkiewicz, S. et al. "Development and Implementation of a Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcer Incidence Tracking System and Algorithm" (2010) 32:44-51.
Commonly perceived as a nursing problem, pressure ulcers (also called decubitus ulcers, bedsores and pressure sores), in reality, are a global healthcare concern. As the global population ages, so does the nursing home population, leading to more pressure ulcers.
Vulnerable patients of pressure ulcers include the elderly, stroke victims, patients with diabetes, dementia, those in wheelchairs, bedridden or suffering from impaired mobility or sensation. Paralysis on the operating room table and sedentary stays in the ICU are also situations that can initiate pressure ulcer development in otherwise healthy patients. Patients 65 years of age and older accounted for 72% of all patients hospitalized during which pressure ulcers were noted.
According to the National Pressure Advisory Panel, a pressure ulcer is localized injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence, as a result of pressure, or pressure in combination with shear and/or friction. Even though the caretaker may try to make a great deal of efforts to prevent pressure ulcer development by trying to relieve pressure, it is still extremely difficult and expensive to adequately and timely relieve pressure.
Although numbers vary widely in the literature, health care costs required to heal a single ulcer have been estimated between $5,000 and $60,000 per ulcer. Moreover, pressure ulcers can be a major source of infection and lead to complications such as bone infection (osteomyelitis), bloodstream infection (septicemia) and death.
Causes of Pressure Ulcers
The most important cause of pressure ulcers is externally applied pressure for an excessive period of time. Other physical influences that can damage the skin include friction at the skin surface, shearing forces (i.e., lateral displacement of the skin, whose layers are of differing firmness), and moisture. Moisture does not cause a pressure injury per se, but it can promote the generation of chronic wounds by softening the upper layers of the skin (maceration) and changing the cutaneous chemical environment (altered pH).
Immobility is the main risk factor for pressure ulcers because patients can no longer regularly take pressure off vulnerable areas of the body by shifting their weight or changing their position. In addition, cardiovascular diseases (peripheral arterial occlusive disease, congestive heart failure) and nutritional problems (cachexia, malnutrition, inadequate fluid replacement) can impair the supply of oxygen and nutrients to peripheral tissue.
Treatment of Pressure Ulcers Often Involves the Following Steps:
- Relieving the pressure that caused it by repositioning the patient regularly and placing him/her in correct positions, and by using adequate support surfaces
- Removing necrotic tissue to inhibit infection and promote healing
- Keeping wounds clean to prevent infection.
- Using proper dressings to promote healing by keeping a wound moist, creating a barrier against infection and keeping the surrounding skin dry
Pressure ulcers are difficult to heal due to many complex issues, including:
- Poor blood circulation (ischemia)
- Excessive moisture and constant contamination from incontinence, perspiration or wound discharge
- Disrupted epidermal barrier and susceptibility to infection
- Infection with antibiotic-resistant biofilms
- Eschar and fibrous tissue formation
- Prolonged inflammation and maceration stalling productive wound healing
- Pain and itch due to bacterial and/or fungal infection
- Difficulty of removing the ulcer-causing pressure from the wound area (off-loading) effectively
Facing these challenges and to improve the speed and quality of healing, one may consider using a multi-functional topical therapy with these features:
- Including ingredients with broad-spectrum anti-microbial properties to protect wound bed from infection and to inhibit formation and growth of bacterial biofilms without harming nascent, delicate regenerating tissue;
- Employing naturally anti-inflammatory and analgesic ingredients to suppress prolonged inflammation and pain;
- Combination with ingredients that promote microcirculation of the low extremities to facilitate autolytic debridement of necrotic tissue and to promote tissue regeneration;
- Ability to absorb wound fluid (exudate) and reduce malodor, and yet maintain a physiologically moist wound healing environment without causing maceration
- Allowing painless and less frequent dressing change;
- Healing wounds fast and effectively with maximum restoration of skin function and minimal scarring to reduce the chance of recurrence.
Note:
Please be advised that the information presented above is not to be used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment of any disease. Statements made about products have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Viewers should not rely solely on the information provided on this web site for their own health problems, and are advised to consult with their physicians or other healthcare providers.
WINVIVO Wound Ointment:
Multi-Functional Botanical Therapy
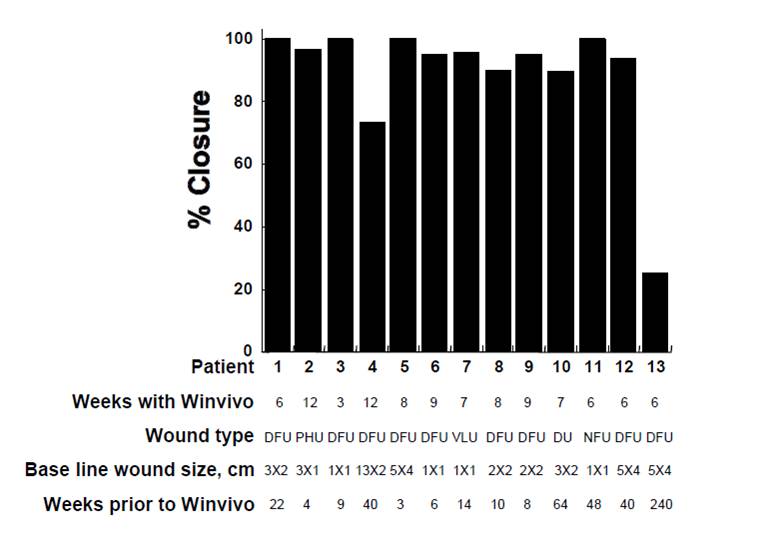
Clinical Studies
- Difficult-to-Heal Wounds
Clinical Case Reports
- Cases #1A-6A
- Cases #1B-8B
- Cases #1C-7C
- Cases #1D-4D
- Cases #1E-2E
- Cases #1F-6F
- Cases #1G-5G
- Case #1H
- Case Series #1I
- Case Series #1J
Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | Return Policy | Contact Us
© 2009-2021 WinVivo Corporation All Rights Reserved