Rhubarb root (Rheum palmatum)
 The dried root of Rheum palmatum is used in the preparation of the WINVIVO Wound Ointment.
The dried root of Rheum palmatum is used in the preparation of the WINVIVO Wound Ointment.
Traditional Uses of Rhubarb Root (Rheum palmatum)
- The first record for medical use of rhubarb has been appeared in the
Chinese medical literature of The Divine Farmer’s Materia Medica (25 A.D. to 220 A.D). - In Traditional Chinese Medicine, rhubarb is used extensively as a purgative to treat a wide variety of accumulations, including constipation caused by excess heat, epigastric distention, fullness.
- Rhubarb has also been used to treat excess heat during high fever, delirium, semiconsciousness and convulsions.
Modern Research - Rhubarb Root (Rheum palmatum)
- Rhubarb root has remarkable purgative effect; and sennoside, aloe-emodin and rhein are components
most responsible of this property. - It also has a) hepatoprotective effects, especially againstcarbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage; b)
hemostatic effects in stopping bleeding; and c) broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially against the streptococcus and staphylococcus strains of bacteria.
In vitro anti-fibrotic activities of herbal compounds and herbs.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Oct; 24(10):3033-41.
Hu Q, et al.
Department of Renal Medicine, King's College London, London, UK.
Abstract
BACKGROUND: We recently developed high-throughput assays of inflammation-independent anti-fibrotic activities based on TGF-beta1-induced total collagen accumulation and nodule formation in normal rat kidney fibroblasts.
METHODS: These assays were applied to examine the anti-fibrotic activities of 21 compounds isolated from plants used in Chinese medicine and methanol extracts of 12 Chinese herbs. Lactate dehydrogenase release assay and cell detachment index were used to monitor cytotoxicity. Changes in fibrogenic molecular markers were observed by reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction and high-content imaging analysis of immunofluorescence.
RESULTS: Three flavonoids (quercetin, baicalein and baicalin) and two non-flavonoids (salvianolic acid B and emodin) demonstrated anti-fibrotic activities in both total collagen accumulation and nodule formation assays. The remaining 16 compounds had little anti-fibrotic effect or were cytotoxic. The anti-fibrotic compounds suppressed collagen I expression at both mRNA and protein levels and also variably suppressed alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. Methanol extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge and Rheum palmatum L., which are rich sources of baicalein, baicalin, salvianolic acid B and emodin, respectively, also showed in vitro anti-fibrotic activities.
CONCLUSIONS: Five herbal compounds and three herbal extracts have in vitro anti-fibrotic activities. These data warrant further studies on these anti-fibrotic entities and suggest it a promising strategy to discover new anti-fibrotic drugs by screening more plant materials.
Emodin inhibits proinflammatory responses and inactivates histone deacetylase 1 in hypoxic rheumatoid synoviocytes.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011; 34(9):1432-7.
Ha MK, Song YH, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Jung JH, Kim B, Song HS, Huh JE, Kim SH.
Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Korea.
Abstract
Chronic inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is promoted by proinflammatory cytokines and closely linked to angiogenesis. In the present study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl-anthraquinone) isolated from the root of Rheum palmatum L. in interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RA synoviocytes under hypoxia. Emodin significantly inhibited IL-1β and LPS-stimulated proliferation of RA synoviocytes in a dose-dependent manner under hypoxic condition. Also, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) revealed that emodin significantly reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), IL-6 and IL-8], mediators [prostagladin E(2) (PGE(2)), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-13] and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as an angiogenesis biomarker in IL-1β and LPS-treated synoviocytes under hypoxia. Consistently, emodin attenuated the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), VEGF, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α), MMP-1 and MMP-13 at mRNA level in IL-1β and LPS-treated synoviocytes under hypoxia. Furthermore, emodin reduced histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity as well as suppressed the expression of HDAC1, but not HDAC2 in IL-1β and LPS-treated synoviocytes under hypoxia. Overall, these findings suggest that emodin inhibits proinflammatory cytokines and VEGF productions, and HDAC1 activity in hypoxic RA synoviocytes.
WINVIVO Wound Ointment:
Multi-Functional Botanical Therapy
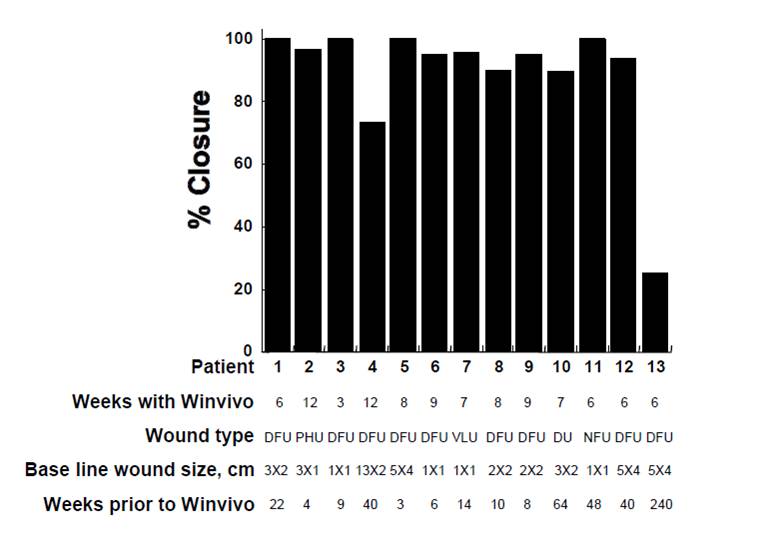
Clinical Studies
- Difficult-to-Heal Wounds
Clinical Case Reports
- Cases #1A-6A
- Cases #1B-8B
- Cases #1C-7C
- Cases #1D-4D
- Cases #1E-2E
- Cases #1F-6F
- Cases #1G-5G
- Case #1H
- Case Series #1I
- Case Series #1J
Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | Return Policy | Contact Us
© 2009-2021 WinVivo Corporation All Rights Reserved